QCon London 2018
Table of Contents generated with DocToc
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for the SWE
- Guardians of the Galaxy - Architecting a Culture of Secure Software
- Insecure Transit - Microservice Security
- Microservices & Scaling of Rational Interactions
- Rust 2018 - an epoch release
- Java at Speed
- Continuous Delivery of Microservices
- Is Boilerplate Code Really So Bad?
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for the SWE
by Rob Harrop
- ML is becoming a competitive necessity
- ML is what’s next for software engineers
- DevOps, uS, containers etc concentration on “how”, ML is about the “what”
- ML still needs good SWE practices - iterations, version control, testing etc
- ML and DevSecOps people need to work together and pull in the same direction
- Skill generalisation vs specialisation
- Individuals specialise, teams generalise
- To learn ML, you don’t need to “first” learn all the theory
- Learning theory after practicing and intuition is easier than learning theory first
- Recommended books
- (No. 1 recommendation) Doing Data Science, Cathy O’Neil & Rachel Schutt
- Hands-on Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn & TensorFlow
- Learning resources
- Coursera Data Science Specialisation - Brian Caffo and Roger Peng
- (Speaker’s favourite) Coursera Deep Learning Specialisation - Andrew Ng
- MIT OCW Linear Algebra - Gilbert Strang
- Coursera Calculus One and Two
- Kaggle - real problem sets to learn ML with
- Beware of bias
- “When a measure becomes a target, it ceases to be a good measure” - Charles Goodhart
- Data bias
- Learned bias
Talk recording: https://www.infoq.com/presentations/ai-ml-swe
Guardians of the Galaxy - Architecting a Culture of Secure Software
by Laura Bell
- Security journey
absent -> ad-hoc -> gated -> agile -> continuous - Good practices to be meet security objectives
- Automation of deployment, provisioning, static analysis, vulnerability management etc
- Autonomy - builder of system is best placed to fix security problems in the system; every person in every SWE team needs the skills, authority and accountability for security
- Integrated into pipeline - has a cost; use dependency checkers, static analysis tools, vulnerability scanners etc
- ensure there is alert noise to keep this effective
- Measurable
- Respectful - every action has a cost, value the time and resource needed to complete an action
- Culture
- Extend blameless culture to security
- Data driven security - patch adoption, upgrade rates, device patterns, browser patterns, error rates,
query times etc
- Some of these are not security metrics, but that’s ok, it doesn’t have to be
Insecure Transit - Microservice Security
by Sam Newman
- Data breach investigation report by Verizon - yearly publication
- 81% of all data breaches are because of bad passwords (stolen or weak)
- Good advise on passwords and management of passwords
- Refer to article by Troy Hunt
- Longer is stronger
- Eliminate complex character composition rules
- Embrace password managers - not just for personal use, but also for your day job!
- Do not mandate password changes, instead monitor for password compromises (How?)
- Check for breached passwords - Troy Hunt’s pwned service
- Three R’s of enterprise security
- Rotate: short-lived credentials
- Repave: patch your stuff
- Repair: if you are not sure, burn it down! Easy with IaaS, repeatable infra and application provisioning
- Test your production back-ups
- Where are your back-ups? Back-up of data stored in a AWS account, stored in the same AWS account? What if an attacker gets access to your AWS credentials and nukes your DB and the back-ups
- Make use of secret stores, example: Hashicorp Vault, AWS Key Management Service
- 44% of data breaches occur due to lack of patching (Source: Forbes), example: Equifax breach due to lack of patching of a vulnerability in version of Struts being used
- Patch hygiene is important - patch cycles have gone down, make sure you keep up
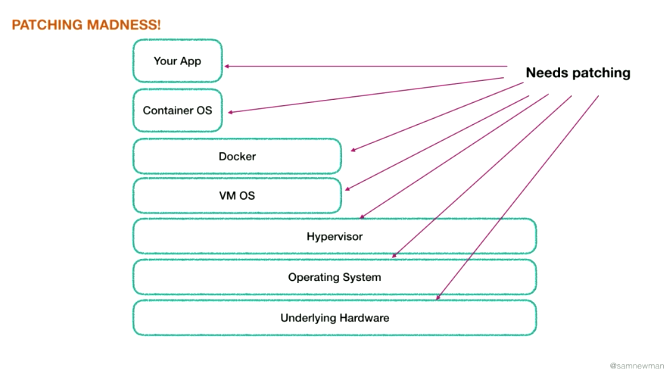
- Understand and implement authN and authZ
- Can use OAuth, JWT etc for authZ
Microservices & Scaling of Rational Interactions
- uS may be lost into obscurity in a few years, not because they will be obsolete, but because they will be second nature and hidden under higher levels of abstraction
- Languages will start taking care of distributed scaling and similar properties of uS
- Promise theory
- Adhering to the public API spec
- An agent can only promise its own behaviours
- Imposition on others is likely ineffective without a promise to accept
- Both receiver and agents have to promise for effect
- Every agent assesses others’ promise from its own perspective
- Dependency on another agent’s promise may make a promised ineffective
- Services make promises, how they are deployed - as a uS or a monolith, doesn’t affect how an outsider views the promises
- Modularity - good for performance? good for aesthetics? good for cognitive thinking?
- Monitoring isn’t evolving at the same pace of modularity
- Monitoring and debugging in a highly modular ecosystem is complicated
Rust 2018 - an epoch release
- Systems programming language, fast, prevents seg faults, guarantees thread safety
- Low level (pointers, mem allocation) and high level stuff can be done
- program an OS
- write command line tools
Java at Speed
- Code goes through stages in the JVM Interpreted -> Tier 1 profiling -> optimised
- Java code is slow to start with and gets faster over time
- JIT compilers know what machine they are running on and thus translate to different machine codes for the same java code
- JMH - tool for uBenchmarking
Continuous Delivery of Microservices
by Sheroy Marker
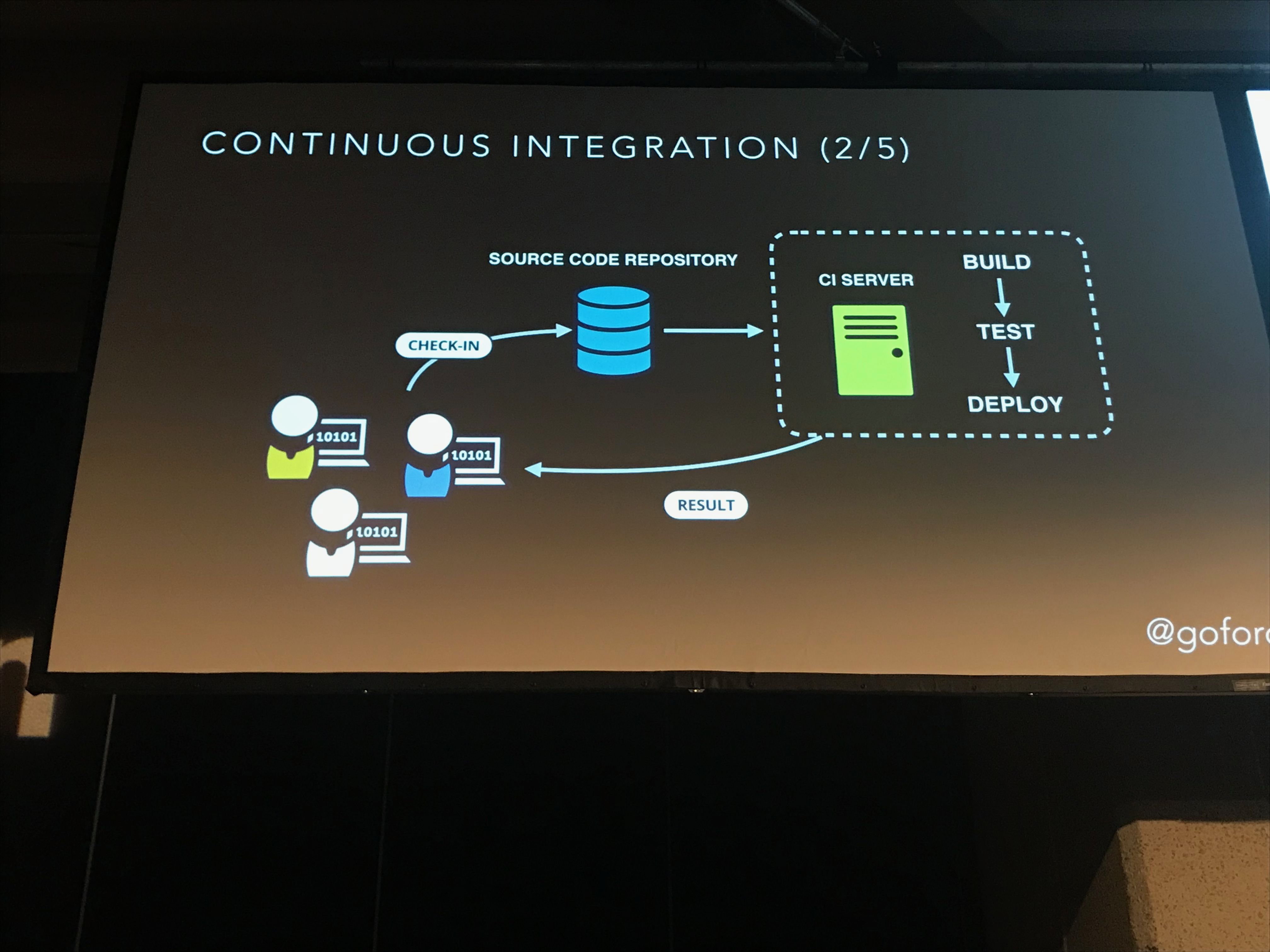
- CD - release quickly and in a sustainable way
- Challenges
- Maintaining integrity of complex distributed systems
- Safely and rapidly releasing features constantly
- Managing deployments od disparate technology stacks
- Considerations
- Test strategy
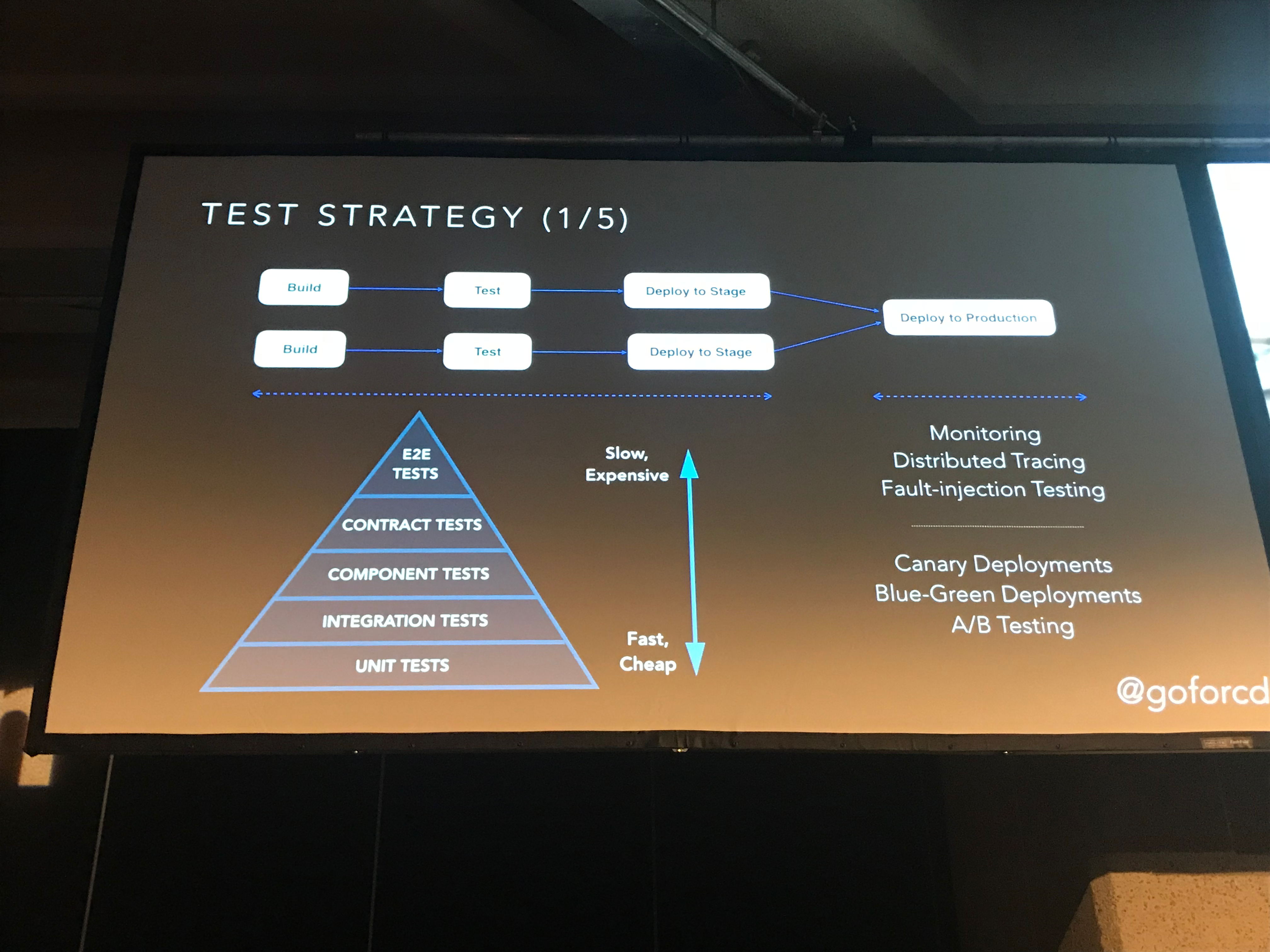
- CI
- Trunk based development - essential to have tests first for this to work, else you might end up having untested code in trunk and thus trunk wouldn’t be releasable. Trunk should always be releasable.
- Feature toggles - should be short lived and should be discarded once feature has been released to prod. These
are tech debt requiring if-else branches. This needs to be cleaned-up on a regular basis.
- Environments - right number and types
- Plan intended use for environments
- Dynamic environment creation
- Managing configuration
- Manage configurations centrally instead of having them spread across chef, code repo, CD tool etc
- Governance process for secrets
- Remediation
- When a pipeline breaks - rollback or roll forward? If quick, roll forward else rollback. Rollbacks are tricky.
- Try maintaining backwards compatibility, esp with DB changes
- Test strategy
Is Boilerplate Code Really So Bad?
by Trisha Gee
- TL;DR - YES!
- Boilerplate can obscure business logic
- Being expressive is better than being terse
- Unnecessary syntax
- semicolons
- new keyword
- anything whose only purpose is to tell the computer what to do and doesn’t contribute towards functionality
- JShell for rapid prototyping and feedback
- Java has moved on in the last 3 years

- IDE generates boilerplate, but when you come back to it you can’t identify auto generated vs custom code
- Code generation is useful but not really the answer
- Kotlin removes a lot of boilerplate, like Java 10, Scala etc
- Java 8 optionals - more readable
- Kotlin: Expressing the lambda definition in the signature of the method
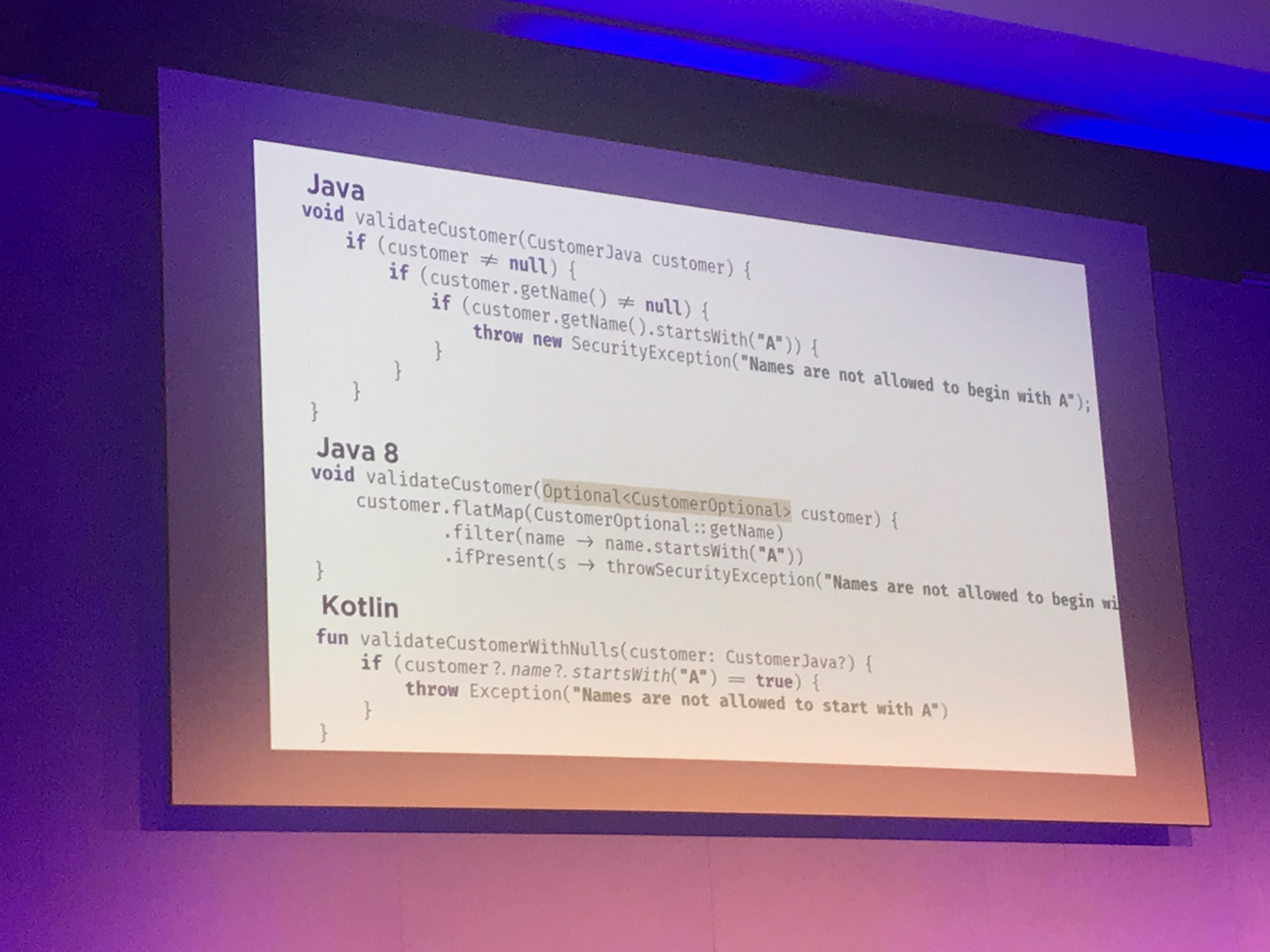
- http://bit.ly/BoilJVM